In recent years, Generative AI has emerged as a revolutionary force in artificial intelligence, providing businesses and individuals with groundbreaking tools to create new data and content.
So, what exactly is Generative AI? The concept refers to a type of artificial intelligence that is designed to generate new content rather than simply analyze or classify existing data. It leverages complex machine learning models to create outputs such as text, images, music, code, and even video by learning patterns from vast datasets.
Generative AI systems, like large language models (LLMs), use sophisticated algorithms to understand context, style, and structure. They can then apply this understanding to craft human-like responses, create art, or solve complex problems. These models are trained on enormous amounts of data, allowing them to capture nuanced patterns and relationships. As a result, they can produce outputs that are often indistinguishable from human-created content–and do it in a fraction of the time as humans.
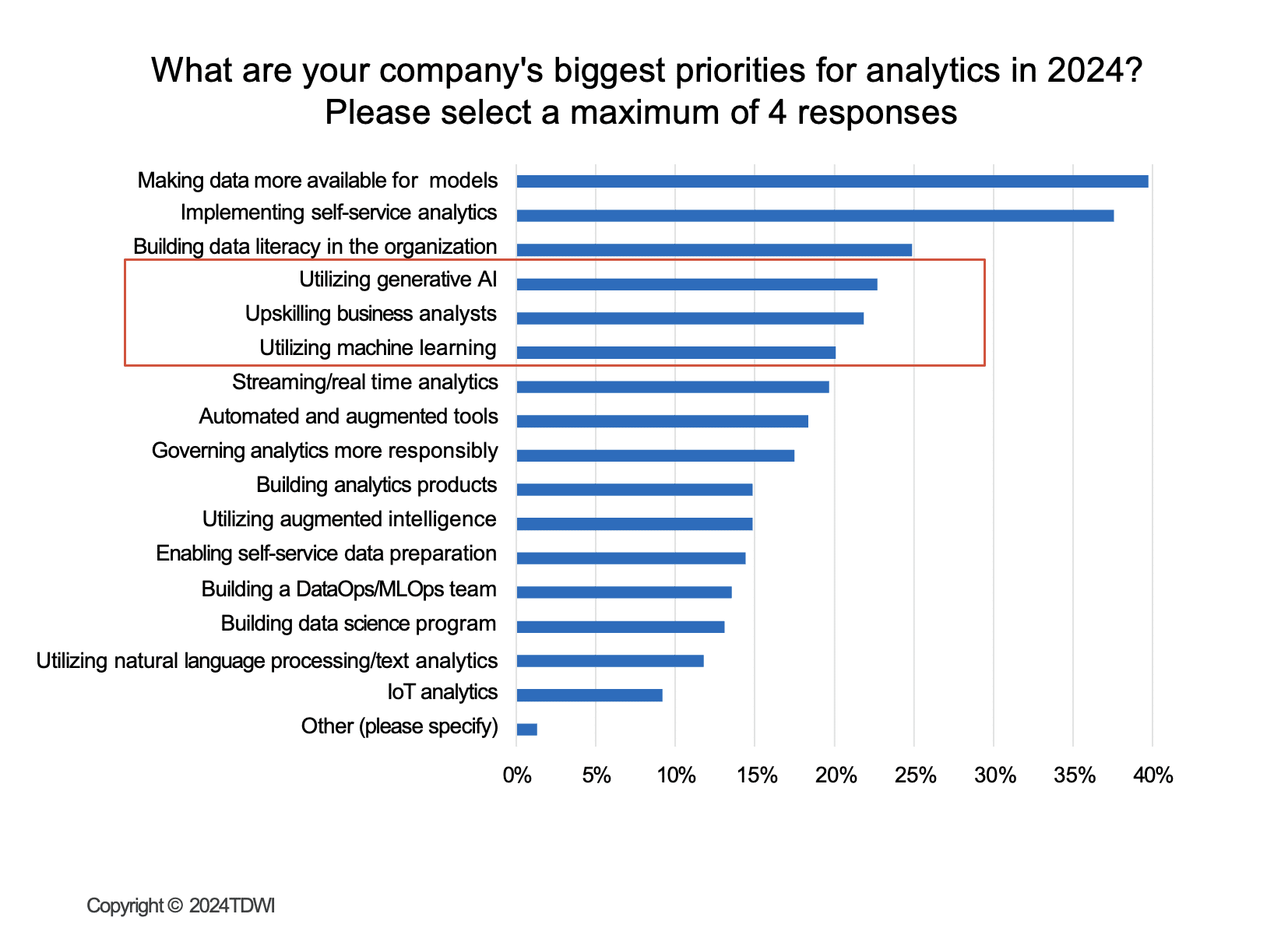
The following survey conducted by TDWI shows that utilizing Generative AI is a major priority for companies in 2024. It ranks alongside other top initiatives like machine learning and upskilling business analysts, indicating that businesses are keen to explore and implement Generative AI technologies to enhance their analytics capabilities.
Given that high level of priority, understanding five core truths around Generative AI helps to demystify its capabilities and limitations while showcasing its transformative potential:
- Generative AI Uses Predictions to Generate Data
At its core, Generative AI leverages predictions made by deep learning algorithms to generate new data, as opposed to traditional AI models that use data to make predictions. This inversion of function makes Generative AI unique and powerful, capable of producing realistic images, coherent text, audio, or even entire datasets that have never existed before.
Example: Consider Generative Pre-trained Transformer, better known as GPT, models that predict the next word in a sentence based on the preceding words. With each prediction, these models generate fluid, human-like text, enabling applications like chatbots, content creation, and even creative writing. This capability is a radical shift from how traditional AI models simply analyze existing data to make decisions or classifications.
Why It Matters: The ability to generate data through predictive modeling opens the door to creative applications, simulation environments, and even artistic endeavors that were previously unimaginable in the AI world.
- Generative AI is Built on Deep Learning Foundations
Generative AI stands on the shoulders of well-established deep learning algorithms such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Transformer models like GPT. These frameworks power the generation of realistic images, text, and other forms of content.
-
- GANs: Used extensively for creating high-quality images, GANs pit two networks against each other—a generator and a discriminator. The generator creates images, while the discriminator judges their quality, gradually improving the output.
- VAEs: These models enable the creation of entirely new data points by understanding the distribution of the data itself, often used in generative tasks involving audio and text.
- Transformers (GPT): The backbone of LLMs, transformers utilize self-attention mechanisms to handle large-scale text generation with impressive accuracy and fluency.
Why It Matters: These deep learning foundations provide the generative power to these models, enabling them to create diverse types of outputs. Understanding these algorithms also helps developers and AI enthusiasts choose the right architecture for their Generative AI tasks, whether for generating art, music, text, or something entirely different.
- Generative AI Stands Out in Conversational Use Cases
A key strength of Generative AI is in applications where humans interact conversationally with AI systems. This differs from traditional AI and machine learning applications, which typically stand out in scenarios where the system is making decisions on behalf of humans. In Generative AI, dialogue-driven interactions come to the forefront.
Example: Chatbots powered by GPT models can converse with users in natural language, answering questions, providing recommendations, or even assisting in customer service. These models shine in areas where continuous interaction with users is essential for delivering valuable outputs.
Why It Matters: The conversational capability of Generative AI redefines user experiences. Instead of using structured, predefined outputs, users can ask open-ended questions and get context-aware responses, which makes interactions with machines feel more fluid and human-like. This represents a monumental leap in fields like customer service, education, and entertainment, where AI needs to respond dynamically to human inputs.
- Generative AI Fosters ‘Conversations with Data’
One of the most exciting developments in Generative AI is its ability to let users have “conversations with data.” Through Generative AI, even non-technical users can interact with complex datasets and receive natural-language responses based on the data.
Example: Imagine a business analyst querying a vast dataset: Instead of writing SQL queries, the analyst simply asks questions in plain language (e.g., “What were the sales in Q3 last year?”). The generative model processes the query and produces accurate, data-driven answers—making analytics more accessible and democratized.
Why It Matters: By lowering the barrier to entry for data analysis, Generative AI makes it easier for non-technical users to extract insights from data. This democratization is a huge leap forward in industries like finance, healthcare, and logistics, where data-driven decisions are crucial, but data skills may be limited.
- Generative AI Facilitates ‘Conversations with Documents’
Another pivotal truth about Generative AI is its capacity to facilitate “conversations with documents,” allowing users to access knowledge stored in vast repositories of text. Generative AI systems can summarize documents, answer questions, and even pull relevant sections from large bodies of text in response to specific queries.
Example: In a legal setting, a lawyer could use a Generative AI system to analyze large case files. Instead of manually combing through hundreds of pages, the lawyer could ask Generative AI to summarize key rulings, precedents, or legal interpretations, greatly speeding up research and decision-making.
Why It Matters: In industries where professionals deal with large amounts of documentation—such as law, medicine, or academia—the ability to have a “conversation” with documents saves valuable time and resources. By providing context-aware insights from documents, Generative AI helps users find specific information without wading through reams of text.
Changing How We Interact with Technology
These truths about Generative AI shed some light on the capabilities and potential of this groundbreaking technology. By generating data through predictions, leveraging deep learning foundations, and enabling conversational interactions with both data and documents, Generative AI is reshaping how businesses and individuals interact with technology.
As we continue to push the boundaries of Generative AI, it is crucial to understand how these truths will shape future applications, driving innovation across industries. Whether organizations are building chatbots, analyzing data, or interacting with complex documents, Generative AI stands as a versatile and powerful tool in the modern AI toolbox. To make sure an organization’s data is ready for Generative AI, get our checklist.
The post Exploring the Fundamental Truths of Generative AI appeared first on Actian.
Author: Steven B. Becker