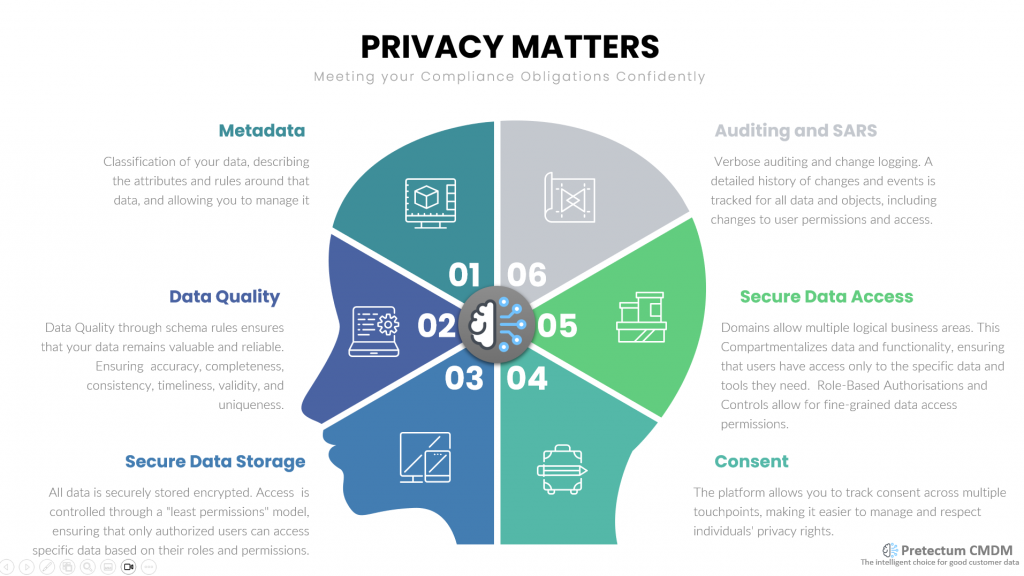
Question your use of Third party data
A FTC Report: “Data Brokers: A Call for Transparency and Accountability” is now ten years old but remains highly relevant today. Over the past decade, the role of data brokers has seemingly expanded, with these entities collecting, analyzing, and selling even greater amounts of personal information. The report initially highlighted the opaque nature of data broker operations and called for greater transparency and accountability. Despite some progress, many of the concerns raised in the report still persist.
Data brokers have even more avenues to gather and monetize information, often without the explicit consent or knowledge of consumers. The regulatory environment has struggled to keep pace with environment change, while legislative efforts have aimed to enhance data privacy at the local and regional level. In the US there is no adequately broad national or Federal legislation and many consumers are still unaware of the extent of data collection and the potential implications for their privacy and security.
In the face of the numerous calls for transparency and accountability, policymakers, industry leaders, and consumer advocates are trying to work together to create robust frameworks that protect individuals’ privacy rights while still supporting innovation. This includes developing clearer regulations, promoting ethical data use, and providing consumers with greater control over their personal information.
Though the FTC report is a decade old, its message continues to resonate.
Big Data is big business
Data brokers continue to amass enormous quantities of information from a multitude of sources, both online and offline. The FTC reported that one particular data broker that they studied had “3000 data segments for nearly every U.S. consumer.” Another’s database covered “one trillion dollars in consumer transactions,” and yet another added “three billion new records each month.”
Data brokers of 3rd party data combine and analyze seemingly unrelated data points to create detailed consumer profiles. They make inferences about consumers, including potentially sensitive ones. “Data brokers combine and analyze data about consumers to make inferences about them, including potentially sensitive inferences.”
Interestingly, even government agencies make extensive use of commercial data brokers’ repositories to gather, analyze, and leverage vast amounts of information for various purposes.
These purposes can include enhancing national security, conducting criminal investigations, tracking financial crimes, and even monitoring public health trends.
By accessing the extensive datasets maintained by commercial data brokers, government agencies can supplement their own data collection efforts and gain insights that may not be available through traditional means. This collaboration can enhance decision-making processes, improve the efficiency of operations, and provide a broader understanding of complex situations.
However, this practice also raises concerns about privacy, data security, and the oversight of how such information is used and shared.
Where they get the data
Data brokers obtain information from a variety of public, commercial and private sources. Federal Data like Census Bureau, Social Security Administration’s Death Master File, U.S. Postal Service, federal courts for bankruptcies and state/local governments such as professional and recreational licenses, real property records, voter registration, motor vehicle records, court records, vital records all form a part of the picture. Some of this information, like voter registration and driving records, has restrictions on commercial use in some states and under federal law (DPPA) but it how it is used to set supplementary data flags may be far from transparent.
While social media platforms offer a way to connect, share, and express ourselves, not all of them prioritize user privacy to the same extent. Some platforms are designed to encourage public sharing, while others may have weaker privacy protections or data practices that expose user content more broadly. Consider these aspects from the top ten social media platforms in the US.
Twitter (X) has tweets as public, visible to anyone on the network, perhaps less so for those without an account but certainly relatively open and unrestricted. While users can set their accounts to private, the platform is designed for open, real-time conversations, making it easy for content to spread widely. Tweets can also be retweeted, quoted, or screenshotted, making it difficult to control how content is shared. Additionally, Twitter itself has faced criticism for data collection and sharing practices.
TikTok is designed for viral content, and videos are often shared publicly by default. The platform’s algorithm encourages widespread visibility, which can make it hard to control who sees your content. TikTok has also faced scrutiny over data privacy, particularly regarding its parent company, ByteDance, and its ties to China. There are concerns about how user data is collected, stored, and potentially shared.
Instagram allows users to set their accounts to private, but the platform is designed for public sharing, especially for influencers and businesses. Stories, reels, and posts can easily be screenshotted or shared without the original poster’s knowledge. Instagram also collects extensive data on user behavior, and its parent company, Meta, has faced criticism for how it handles user data and targets ads.
Facebook offers privacy settings, its default settings often favoring public sharing. The platform’s complex privacy controls can make it difficult for users to fully understand who can see their content. Plus, Facebook has been involved in numerous data privacy scandals, including the Cambridge Analytica incident, where user data was harvested without consent. The platform also tracks user activity across the web for ad targeting.
Snapchat is known for its disappearing messages, the platform’s public features, like Snap Map and public stories, can expose user content and location data to a wider audience. Snaps and messages can also still be screenshotted or saved without the sender’s knowledge. Snapchat has also faced criticism for its data collection practices and sharing with third parties.
YouTube as a public platform by design, has most videos accessible to anyone. Even if you upload unlisted videos, they can still be shared or discovered through direct links. In addition, YouTube collects extensive data on viewing habits and uses it for ad targeting. Comments and interactions on videos are also public by default.
LinkedIn, though a professional networking platform, much of the content shared (e.g., posts, comments, and profile information) is public or visible to your network. Even private messages can be subject to data collection. LinkedIn also collects and shares user data with third parties for advertising and analytics, and tracks user activity across the platform.
Reddit serves as a public forum where posts and comments are visible to anyone unless they are made in private subreddits. Even then, content can be screenshotted or shared outside the platform. And, while Reddit allows for anonymous usernames, the platform still collects data on user activity and interactions, which can be used for ad targeting.
Pinterest is designed for public sharing of ideas and content, and pins and boards are visible to anyone unless explicitly set to private, and even then, they can be shared or repinned. Pinterest also collects data on user preferences and activity to personalize content and ads, raising concerns about how this data is used and shared.
Twitch as a live-streaming platform has most streams as public and accessible to anyone. Even if you set your stream to private, clips and highlights can be shared widely. Twitch also collects data on viewer behavior and interactions, and there have been instances of data leaks exposing sensitive information.
General Privacy Tips for Social Media Users
- Review Privacy Settings: Regularly check and adjust the privacy settings on your accounts to control who can see your content.
- Be Mindful of What You Share: Assume that anything you post online could become public, even on platforms with strong privacy features.
- Limit Third-Party Access: Avoid linking social media accounts to third-party apps or services that may misuse your data.
- Use Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Protect your accounts from unauthorized access.
- Consider Alternative Platforms: If privacy is a top concern, explore platforms like Signal (for messaging) or Mastodon (for social networking), which prioritize user privacy.
Commercial Data Sources
Merchant and financial service company clients, registration websites, and online advertising networks play a significant role in the ecosystem of data exchange and monetization. These entities frequently engage in negotiations and transactions with data brokers, leveraging their access to vast amounts of consumer data. These interactions often occur on a quid pro quo basis, where data is exchanged for services or insights that benefit both parties involved.
Data brokers, known for their expertise in collecting, analyzing, and selling data, enter into a variety of contractual agreements with these sources. These agreements can take several forms, including data supply agreements, licensing agreements, and reseller agreements. Each type of agreement specifies critical details such as the nature of the data being provided, the methods of data transfer, how frequently the data will be updated, and any restrictions on how the data can be used.
Through these agreements, data brokers gain access to a wide range of data, which they then process and enhance to create valuable products. These products are developed using two main types of data: “actual data elements” and “derived data elements.” Actual data elements refer to the raw, unprocessed data collected directly from the source, such as a consumer’s name, address, or purchase history. Derived data elements, on the other hand, are insights or inferences drawn from the raw data. These might include behavioral predictions, preferences, or interests.
For instance, by analyzing various data points, a data broker might infer that an individual who holds a boating license likely has an interest in boating activities. This inference can be invaluable to businesses in the maritime industry looking to target potential customers with tailored marketing campaigns. By combining actual and derived data, data brokers can offer nuanced and targeted insights that help businesses make informed decisions and optimize their marketing strategies.
Overall, the collaboration between merchant and financial service company clients, registration websites, online advertising networks, and data brokers exemplifies the intricate web of data exchange that fuels the modern digital economy. This system relies on a complex framework of agreements and data processing techniques to transform raw data into actionable insights that drive business growth and innovation.
Data Products
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) identifies three main categories of data products offered by data brokers, each with distinct characteristics and regulatory considerations.
Marketing Products – designed to help businesses and organizations target consumers with advertisements and promotional offers. The data often includes demographic information, purchasing behavior, interests, and lifestyle preferences.
Regulatory considerations for marketing products typically focus on consumer privacy and consent, ensuring that data collection and use comply with laws such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA).
Risk Management Products – used primarily for assessing risks associated with financial transactions, insurance underwriting, fraud detection, and identity verification. Data brokers provide information that helps businesses evaluate the creditworthiness or reliability of individuals. Regulatory considerations for risk management products often involve strict compliance with the FCRA, which dictates how consumer information can be used in credit reporting and related activities. These products can also assist in identifying potentially fraudulent transactions or activities by matching and analyzing consumer data.
Some of this used to help clients verify consumer identities, often to comply with regulations like the USA PATRIOT Act customer identification requirements. This can involve confirming information or indicating an individual’s status (e.g., active duty military). Data brokers typically use Social Security Numbers (SSN) internally for these products but do not share them with clients.
People Search Products – generally used to locate individuals and gather information about them for various purposes, such as background checks, reconnecting with lost contacts, or verifying identities. The data collected may include addresses, phone numbers, social media profiles, and other personal details.
Regulatory considerations for people search products focus on ensuring accuracy, transparency, and respecting individuals’ rights to access and correct their information, as well as adherence to privacy laws that restrict the sharing of sensitive information without consent.
Shadow Data Brokers – some data brokers not part of the FTC study reportedly sell lists based on sensitive health conditions or professions. others facilitate targeted advertising online through techniques like “onboarding” (matching offline data with online identities using email addresses and cookies). Such a process involves segmenting, matching, and targeting consumers on various websites and social media platforms; they may also offer services to predict consumer behavior, such as scores indicating the likelihood of responding to specific marketing efforts or having undeliverable mail.
Each category has unique implications for privacy, data security, and ethical use, requiring data brokers to navigate a complex landscape of regulations to ensure compliance and protect consumer rights.
Data Quality & Control
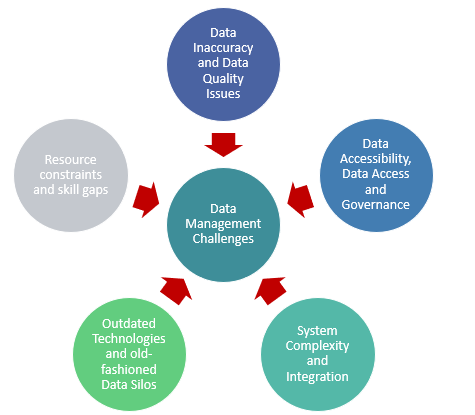
The FTC has outlined concerns about the accuracy of data broker information across all product types (marketing, risk mitigation, and people search) but part of the challenge is that data brokers serve a wide array of clients across various industries, including retail, financial services, marketing/advertising firms, government entities, and more, the lack of rigid regulation has also meant that client screening, contracting, and monitoring practices vary among data brokers, depending on the product type.
For the consumers, some data brokers offer opt-out mechanisms, but these may not be comprehensive or easily accessible. Information might still appear in other contexts or through other data brokers. Consumers generally have fewer controls over data used for risk mitigation due to its connection to legal and regulatory compliance (e.g., identity verification). While some brokers may offer opt-out for inclusion in search results, this doesn’t necessarily remove the underlying public record information.
Consumers also often lack a complete understanding what data is collected, how it’s used, and how to exercise any available rights. Opting out with a slightly different name might for example, not capture/cover all stored records.
The report paints a comprehensive picture of the data broker industry, emphasizing its significant reach, the vastness and potential sensitivity of the data handled, and the considerable implications for consumer privacy and well-being.
The report also strongly advocates for increased transparency and accountability through legislative measures and industry best practices to empower consumers with greater control over their personal information in this complex data-driven landscape. The supplemental information serves as a glaring reminder of the tangible ways data brokers operate and the potential consumer privacy and business (and government) decisioning vulnerabilities their practices can expose.
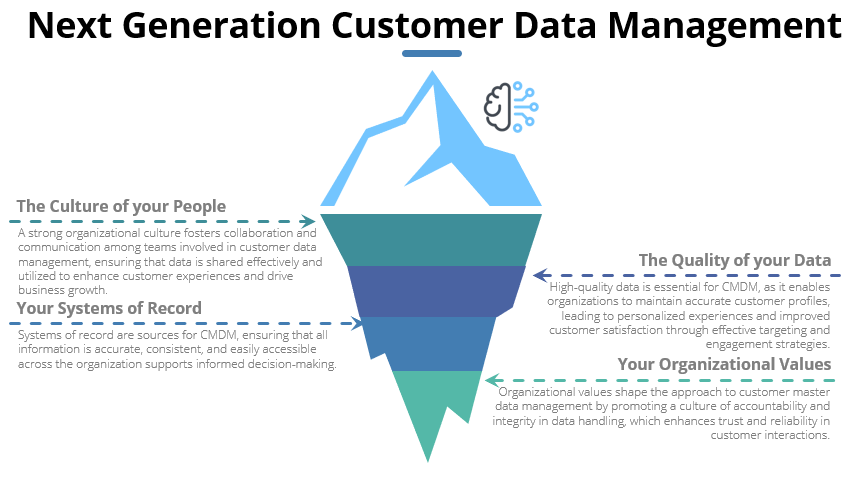
If your business wants to move away from third party data use and focus on zero and first party data and data management you should look at the Pretectum Customer Master Data management platform with consent today!









