The future for ERP in 2023
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software solutions have been a crucial tool for businesses of all sizes for several decades now.
ERP software like SAP, Oracle Business Suite, NetSuite and Microsoft Dynamics have helped organizations manage their resources more effectively, streamline operations, and make data-driven decisions.
As businesses have become more data-driven, the demand for easy-to-use tools to analyze and visualize data will increase. Consumer grade user experiences have become table stakes for ERP vendors trying to retain market share or garner attention from new audiences.
Tech advances, particularly cloud tech, and the accompanying business landscape do make the future of ERP software solutions uncertain.
Legacy on-premise ERP systems are also typically more expensive upfront, require specialized IT staff to maintain, and may have limited scalability. Upgrades and updates may also be more time-consuming and expensive than with cloud ERP.
The current trend in ERP software is towards more cloud-based solution adoption.
Cloud-based ERP software offers several benefits over traditional on-premises solutions, including reduced costs, improved scalability, and increased accessibility. With cloud-based solutions, companies no longer need to invest in expensive hardware, software, and IT personnel.
Cloud-based ERP solutions are also often highly scalable, allowing businesses to easily add or remove users and features as needed. Finally, cloud-based ERP solutions are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, making them ideal for remote work and global operations.
Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities is also increasingly becoming a part of the selection criteria and blockchain is considered to have some potential.
Both of these technologies can help businesses automate routine tasks, analyze vast amounts of data, and provide valuable insights. AI and ML help businesses identify patterns and trends that would often be difficult or impossible to discern manually. This, all in its turn, helps businesses make more informed decisions and optimize their operations for maximum efficiency.
The heritage ERP vendors are likely to continue to invest heavily in improving the user experience of principally their newer software most of which is cloud focused, to make it easier for business users to access and understand data.
One of the biggest challenges facing ERP vendors in this wave of forced techstack renewal is the need to balance flexibility with standardization. Customization of solutions that meet their unique needs has long been discouraged, it creates compatibility issues when integrating with other systems and makes the platform difficult to upgrade. ERP vendors are having to look long and hard at how they build to work out just how customizing can be adequately supported without becoming a nightmare of the future
Another challenge is the increasing demand for real-time data. Modern business practices are heavily data-driven, they have a need for real-time data to support agility and responsiveness. ERP solutions have often been bound up in batch based processes and now they have to find a way to provide real-time data without sacrificing data accuracy or system performance.
Cloud ERP and legacy on-premise ERP systems have their own advantages and disadvantages. It’s not a matter of one being “as good as” the other, but rather which solution is more suitable for a specific business.
Cloud ERP systems are becoming increasingly popular because they offer several benefits, such as lower upfront costs, scalability, accessibility, and automatic updates. With cloud ERP, businesses don’t need to worry about hardware maintenance or software updates, as the cloud provider takes care of everything.
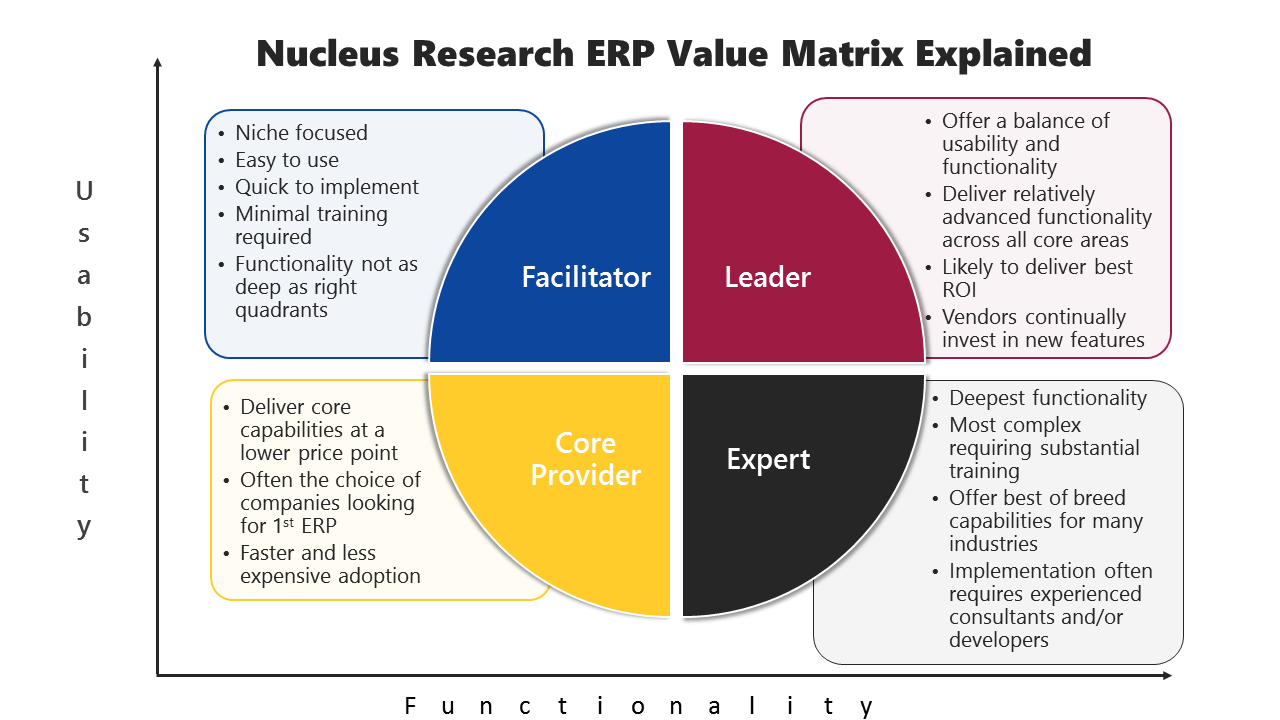
Nucleus Research provides a ERP Value Matrix as a tool developed by them to evaluate ERP vendors and solutions based on two primary factors: usability and functionality.
The matrix places ERP vendors in one of four categories: Leaders, Experts, Facilitators, or Core Providers, based on how they perform on these two factors. The matrix also takes into account other factors such as total cost of ownership (TCO), customer support, and innovation, to provide a comprehensive evaluation of each vendor.
The matrix provides businesses with an objective assessment of ERP vendors, helping them to identify which vendors and solutions are the best fit for their needs. By evaluating vendors based on their usability and functionality, businesses can better understand how each solution will impact their operations, and choose the solution that provides the best value for their organization.
The research offers two angles also, a SMB ERP Technology Value Matrix and the Enterprise ERP Technology Value Matrix for business targeting organizations with over $500M in annual revenue. The last assessment was mid 2022 and another is likely June 2023.

Some of the more popular heritage ERP solutions are also offered as ERP solutions but its worth considering the main players in the cloud space right now.
Acumatica – Acumatica’s cloud ERP solution is designed to provide a flexible and customizable platform for small to mid-sized businesses, delivering real-time insights and improving business efficiency.
Epicor ERP – Epicor’s cloud ERP solution combines industry-specific functionality with a modern cloud delivery model to help manufacturers grow their business and streamline their operations.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 – Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a cloud-based ERP system that offers a range of modules for financial management, supply chain management, and project management. It also integrates with other Microsoft products such as Office 365 and Power BI for advanced analytics.
NetSuite – NetSuite’s cloud ERP solution provides businesses with a single, integrated platform for financial management, supply chain management, and CRM, helping to improve business efficiency and accelerate growth.
Oracle Cloud ERP – Oracle Cloud ERP is a cloud-based ERP system that provides a range of financial management, procurement, project management, and supply chain management tools. It also offers analytics capabilities and integrates with other Oracle cloud products such as Oracle HCM and Oracle CX.
Plex Systems – Plex Systems’ cloud ERP solution is designed specifically for manufacturing organizations, providing real-time insights into production processes and supply chain operations.
Rootstock Cloud ERP – Rootstock’s cloud ERP solution is built on the Salesforce platform and provides a range of manufacturing, supply chain, and financial management tools for businesses of all sizes.
Sage Intacct – Sage Intacct’s cloud ERP solution is designed for small to mid-sized businesses, providing a range of financial management and accounting tools that are customizable and scalable.
SAP S/4HANA Cloud – SAP S/4HANA Cloud is a cloud-based ERP system that provides a range of modules for financial management, procurement, sales, and distribution. It also provides advanced analytics capabilities and is built on the SAP HANA in-memory database platform.
Workday Financials – Workday Financials is a cloud-based ERP system that provides a range of financial management tools, including accounting, procurement, and financial reporting. It’s designed for medium to large enterprises and offers real-time insights into financial performance.
Security concerns, potential downtime, and limited customization options are likely to remain ongoing concerns. Those businesses that require highly specialized or industry-specific functionality may find that a cloud ERP system simply doesn’t meet their specific needs and many on existing on-premise platforms will struggle to make the migration to the cloud.
Read More
Author: Clinton Jones
