The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Business Operations
Artificial Intelligence (AI), today more than ever before, stands out as a transformative force reshaping the way businesses operate.
Like all modern technologies, it has infiltrated many aspects of business, enhancing efficiency, improving customer experiences, and driving innovation. It’s touch, is felt from customer service to data analytics.
AI is revolutionizing traditional approaches and propelling organizations into a new era of possibilities but it is challenged by concerns about bias, transparency and its ability to hallucinate.
Some history
The Turing Test, proposed by British mathematician, computer scientist and codebreaker Alan Turing in 1950, was considered a measure of a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from that of a human.
The test serves as a rudimentary benchmark for assessing a machine’s capability to display human-like intelligence in natural language conversation but the latest developments with Large Language Models (LLMs) and how they naively behave may have most broken the fundamentals of this test and we may need to think of new ways to assess AI.
The basic premise of the Turing Test is to assess a machine’s ability to engage in human-like conversation, that’s still relevant, but its applicability and limitations have become more pronounced in the context of LLMs. LLMs don’t actually understand what you’re saying or asking.
Despite all this, one of the most significant impacts of AI on business operations is evident in customer service. The very space where we want a conversation, may be better served by an AI.
Chatterbots
The reason may be quite simple. We’re not actually looking for a social conversation with an AI when we use a chatbot or a virtual assistant, instead we’re looking for information, or answers to solve the thing that has brought us to the chatbot in the first place.
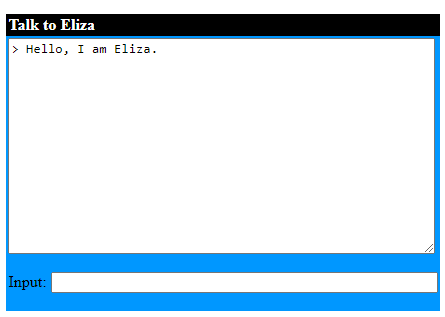
The first “chatterbot” is reputed to be ELIZA, created in the mid-1960s by Joseph Weizenbaum, a computer scientist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
ELIZA operated by processing user responses to supplied prompts and generating pre-defined, contextually appropriate replies.
Using a combination of pattern matching and simple keyword recognition techniques it simulated a Rogerian psychotherapist.
Although the interactions were relatively basic, ELIZA’s ability to mimic human conversation and provide responses that seemed meaningful and engaging was groundbreaking at the time.
If you’re interested, there is a javascript version of ELIZA originally written by Michal Wallace and significantly enhanced by George Dunlop that you can try out at the CSU Fullerton Psychology Department.
When applications are integrated with NLP capabilities, the application “understands” and processes human language. This feature can be part of augmentation of chatbots and virtual assistants and facilitates interactions with customers, employees, and others. Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI-driven RPA can engage in natural language conversations, answer queries, and provide assistance, enhancing customer service and user experience.
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants have come a long way and are just starting to revolutionize the way businesses interact with their customers. With instant responses to customer queries, personalized recommendations, routine task handling, they can ensure a relatively seamless customer experience.
The process robots are coming
An area I have dipped in and out of at various points in my work career since Y2K, is robotic process automation (RPA). The goal of the RPA being to automate mundane and repetitive tasks. Tasks that were previously low value and time-consuming for employees. Early RPAs were very prescriptive and simplistically programmed but today they are amore adaptive. One of the earliest examples of RPA-like automation can be traced back to the introduction of screen scraping software in the 1990s.
AI-driven RPA goes beyond basic task automation by incorporating so called cognitive capabilities. With machine learning (ML) algorithms, RPA systems can analyze vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make decisions based on historical and real-time information. This “cognitive” automation allows businesses to automate complex tasks that require decision-making, such as data analysis, customer service interactions, and fraud detection.
AI in fraud detection, risk management, and algorithmic trading has machine learning algorithms analyze financial data in real-time, identifying unusual patterns and potential bad actor activities, thereby enhancing security and minimizing financial losses.
RPA integrated with AI can excel in processing unstructured data, such as invoices, forms, and emails. Through Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and machine learning, such systems can extract relevant information from documents more accurately than people and faster! This capability streamlines document-based processes, such as invoice processing and claims management, reducing manual errors and improving overall document handling efficiency.
Automation liberates human resources, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of their roles; the kinds of applications include dataentry, invoice processing, and report generation are now handled efficiently by AI-driven systems, leading to higher productivity and reduced operational costs.
Smart reporting
AI has been transforming data analysis for a while now, by enabling businesses to glean improved insights from vast datasets.
Machine learning algorithms analyze historical data, identify patterns, and predict future trends with remarkable accuracy. This predictive analytics can help a business make better informed decisions, optimize inventory practices, more precisely forecast customer demands, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
AI-driven applications optimizing supply chain operations look to historical sales data, market trends, and weather patterns, for example, to predict demand more accurately.
This multi-threaded predictive capability aids businesses in avoiding stock-outs, reducing inventory holdings, and minimizing waste. AI-powered algorithms are also used to optimize route planning and delivery scheduling, which can all improve the effectiveness and cost profile of logistics operations.
By combining data analytics with AI, businesses automate their data analysis and generate more precise actionable insights. AI-driven analytics systems process vast datasets, identify trends, and provide answers in near real-time. Decision-makers now have timely and accurate information, enabling them to make better informed choices to drive business growth and innovation.
More business focus areas
The examples cited above are probably the areas I have seen benefits more commonly from AI in the business setting, but there are at least almost a dozen more that can be considered.
AI algorithms that analyze customer behavior and preferences, enable businesses to create highly targeted marketing campaigns. The campaigns might include personalized recommendations, content, and advertisements to enhance customer engagement and increase conversion rates.
Healthcare professionals have started to consider the use of AI in diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images, and predicting patient outcomes. Machine learning algorithms can process vast amounts of medical data, leading to more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
Analysing medical images, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, lab slides and mammograms, AI, can process these artefacts at speeds much faster than human medical professionals. Algorithms can quickly identify patterns, anomalies, and potential areas of concern.
Subtle changes in medical images that might not be immediately apparent to human eyes are more easily indetified by AI. This early detection can lead to the diagnosis of diseases at their nascent stages, improving the chances of successful treatment and recovery. This is particularly crucial in diseases like cancer, where early detection significantly improves patient outcomes. In critical cases, rapid analysis can be life-saving.
Intelligent tutoring and educational systems adapt to learner styles, providing customized educational content and feedback. AI also aids in automating the administrative tasks for educational institutions, improving efficiency.
In manufacturing and operations, the use of AI can assist businesses in anticipating equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
In talent acquisition processes, automating resume screening, candidate matching, and even conducting initial interviews can accelerate candidate evaluation. Chatbots powered by AI handle the routine HR inquiries, HR professionals focus on more strategic and higher value tasks like employee engagement and development.
AI is employed in environmental monitoring and conservation efforts to predict natural disasters, monitor pollution levels, and aid in wildlife conservation, contributing to more effective environmental preservation strategies.
Legal assistance tools that are AI-powered can help legal professionals in document review, contract analysis, and legal research. Natural Language Processing algorithms enable these tools to process and analyze large volumes of legal documents efficiently, improving accuracy and saving time for lawyers and paralegals.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a transformative force revolutionizing various aspects of business operations. From customer service to data analytics.
AI-driven technologies have significantly enhanced efficiency, improved customer experiences, and driven innovation across diverse sectors.
However, the rapid integration of AI in business processes has raised concerns regarding bias, transparency, and the ability of AI systems to comprehend human-like conversations, especially in the context of Large Language Models (LLMs).
The traditional Turing Test, once a benchmark for assessing machine intelligence, now faces challenges due to the complex behavior of LLMs, prompting the need for new evaluation methods.
Despite these challenges, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants have reshaped customer interactions, providing instant responses and personalized recommendations, thereby ensuring seamless customer experiences. AI-driven Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has automated mundane tasks, liberating human resources and enabling employees to focus on strategic and creative aspects of their roles.
AI has revolutionized data analysis, supply chain optimization, healthcare diagnostics, education, talent acquisition, environmental monitoring, and legal assistance, showcasing its vast potential in diverse business focus areas.
As businesses continue to harness the power of AI, it is imperative to address the ethical concerns and develop innovative solutions, ensuring that AI remains a valuable asset in shaping the future of business operations.
Read More
Author: Clinton Jones