Finding the right home for your customer master
At the intersection of optimal business operations and the discipline of appropriately aligned data governance principled master data management lies Customer Master Data. The practice includes dimensions that define the needs of the business including contact information, customer vitalstatics and pretty much any data attribute that the business needs to leverage for a perfectly harmonized customer relationship.
That’s the dream, unfortunately, the reality is that for many organizations, their data governance practice is mired in conflicting interests of largely divergent stakeholders. There is also the challenge of inter-divisional competition of who owns the customer, and the proverbial data silos that arise from divergent divisional needs.
Some business applications, designed with specific and often narrow objectives in mind, operate within a confined scope of customer data requirements. These applications might be tailored for singular functions such as order processing, billing management, or customer support. In such instances, the focus is primarily on the immediate and specific needs of the application, and the depth of customer data required is limited to the operational necessities of that particular function. While this makes for efficient data processing at the business unit level, it retards opportunities for the whole organization which suffers from the lack of a single identity for the customer with all the salient attributes that make for personalized long-lasting and loyal relationships.
Recognizing the indispensability of a comprehensive customer master, some organizations will embark on a comprehensive rethink of their customer master data management practice. Doing so is a strategic decision and as such, requires a strategic approach to constructing a single, authoritative source of truth for the customer master data information asset accompanied by improved integrations and change management.
Practice not technology
Modern-day Customer Master Data Management also isn’t about the technology as much as it is a realignment of business principles around the most appropriate way to handle the customer and customer data, especially these days in the face of so many emerging and established privacy and consumer protective regulations.
Consider if you will, the fact that how and what you store and nurture as a customer data repository reflects the true essence of your company’s identity. Store it incomplete, haphazardly and with duplicates and you’re relating a narrative that suggests that you simply don’t care too much about data quality and the integrity of the customer master.
Think of the customer master as a reservoir of knowledge that if established properly, can deliver insights, smooth transaction processing, hone personalization and convey confidence and integrity in your team’s engagement with the customer. All this can be done on demand, providing a foundation for robust operational and financial structures. Depending on your industry and the relative intimacy of the relationship with the customer, your business may tap into that reservoir and find previously unexplored areas of opportunity and relationship sustainment.
If you’re in finance or sales, it is easy to see customer data management as a ballet of numbers, for marketing. logistics, service and support it might be other business intricacies like past engagements, previous purchases, warranties, returns and the like. For some, it may even just be about the legitimacy and legalities associated with the customer and their data.
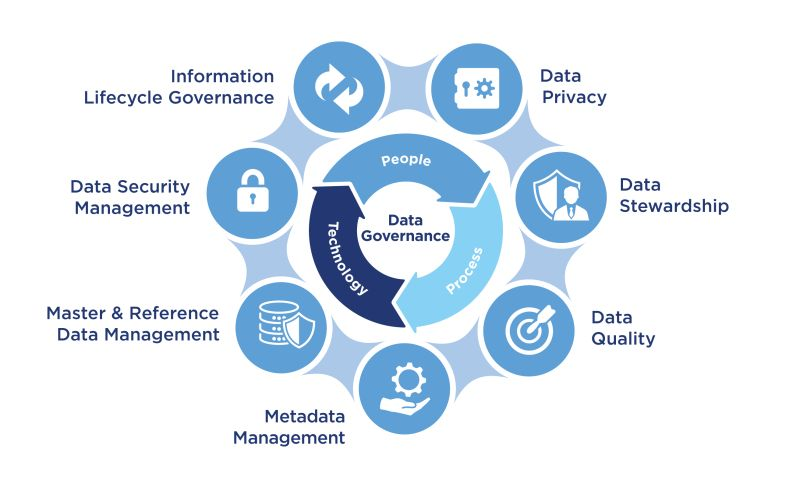
Data governance is the systematic management, control, and oversight of customer-related information within a given organization.
Data governance involves the establishment and enforcement of policies, procedures, and standards to ensure the accuracy, integrity, and security of customer data throughout its lifecycle. The primary goal is to enhance the quality of customer information, facilitate compliance with regulations, and support reliable decision-making processes across the organization.
In his domain, this includes defining roles and responsibilities, implementing data quality measures, and establishing protocols for data access, usage, and privacy.
Some fundamentals
Meticulous management of data quality entails a systematic and detailed approach to ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data within an organization. It involves implementing rigorous processes and practices to identify, rectify, and prevent errors, inconsistencies, and redundancies in the data.
The objective is to cultivate a dataset that serves as a trustworthy foundation for decision-making processes, minimizing the risk of misinformation and supporting the organization’s overall goals. This involves continuous monitoring, validation, and improvement efforts to uphold a high standard of data quality throughout its existence.
Security and privacy in the context of customer master data involve systematically implementing measures to protect sensitive customer information from unauthorized access, misuse, and breaches.
This would encompass the establishment and enforcement of policies, procedures, and controls to safeguard customer data against potential threats. The primary goal is to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of customer information, aligning with relevant data protection regulations.
Security and privacy measures also include access controls, encryption, authentication protocols, and ongoing monitoring to detect and respond to any potential security risks. The objective is to create a robust framework that instils confidence in customers, mitigates risks, and upholds the organization’s commitment to data protection.
Data lifecycle management (DLCM) is an integral component of data governance and involves a systematic and comprehensive approach to handling customer data from its creation or acquisition through various stages of utilization, storage, and eventual disposition or archival.
This essential process ensures that data is managed efficiently and in alignment with the organizational objectives and legal obligations of the organization. A DLCM framework includes the formulation of policies, procedures, and standards to govern the handling of data at each stage.
The primary goal of DLCM is to optimize the utility of data while also addressing issues related to data storage, access, and compliance. It requires organizations to define clear retention policies, in particular, specify how long data should be retained based on its value and regulatory requirements. DCLM also involves establishing protocols for secure data disposal or archival once it has fulfilled its purpose.
Executing a DLCM practice well, involves continuous monitoring, assessment, and adaptation of policies to align with changing business needs and regulatory landscapes. This structured approach ensures that data remains a valuable asset throughout its journey within the organization and is managed with efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and compliance in mind.
Thinking about the people
At the heart of any data governance program are people who may or may not be explicitly tagged as the data governance stewards. These are individuals or teams entrusted with the responsibility of maintaining data quality, upholding governance policies and serving as the data owners and people “in the know” about all things about the data. They are the data domain experts.
Data stewards navigate the vast seas of data, ensuring that each byte is accounted for and that each dataset aligns with the broader goals of the organization. They are the custodians of the data practice.
A more explicit definition would have it, that a data steward is an individual or team responsible for overseeing the management, quality, and governance of data within the organization.
Duties include ensuring data accuracy, defining and enforcing data policies, and maintaining the integrity of data assets. Data stewards play a crucial role in facilitating communication between business units and IT, acting as custodians of data quality and providing expertise on data-related matters.
Their responsibilities encompass data profiling, monitoring, and resolving data issues, as well as collaborating with other stakeholders to establish and adhere to data governance policies. The role requires accountability for the reliability and usability of data across the organization.
Metadata matters
The descriptive information about the customer data, data that provides context, structure, and understanding of its characteristics, is metadata. Such information includes details about the origin, usage, format, and relationships of data. In any data governance program, metadata plays a crucial role in enhancing data discoverability, usability, and overall management.
For customer master data management, metadata associated with customer data would include information about data sources, data quality, and any transformations or processes applied to the data. It helps in maintaining a comprehensive understanding of customer data, ensuring its accuracy and facilitating effective data governance.
For data governance, metadata serves as a bridge between stakeholders and systems. It facilitates collaboration by offering a common language for business users, data stewards, and IT professionals. Stakeholders leverage the metadata to comprehend the meaning and lineage of the customer data, converging on a shared understanding for everyone across the organization. Metadata also enhances the interoperability of systems by providing a standardized framework for data exchange and integration, promoting consistency and coherence in the data landscape.
No respected data governance program is launched, adopted and survives without data governance and management policies. Data Governance policies define who can access specific data, how it can be used, and under what circumstances. These policies form a framework that prescribes how to prevent unauthorized access and ensures responsible data utilization as well as other behaviours and measures that serve to protect the integrity of the customer master.
A data governance council or committee overseeing and steering the program is helpful but not essential. Comprising representatives from various business units and the IT realm, this body ensures that data governance aligns with organizational objectives, and its impact is felt across the entire enterprise.
Fostering a culture of data awareness and responsibility becomes a crucial act in this governance play. Communication and training programs under the aegis of a data governance program are the conduits through which employees grasp the importance of data governance, the program aims to develop an understanding of their roles in maintaining data quality and integrity.
Culturally a data governance program requires a major shift where each employee becomes informed and empowered as a guardian of the data they interact with, hopefully thereby recognizing its intrinsic value.
Continuous improvement in data governance is another essential trait of a data governance program which is sustained through a dynamic and iterative process that prioritizes refinement, adaptability, and ongoing assessment.
Continuous improvement involves regular evaluations of data quality, security protocols, and adherence to established policies.
Organizations that foster a culture of feedback, with data stewards and relevant stakeholders providing insights into the efficacy of existing practices are the most successful.
Insights from continuous improvement initiatives guide adjustments to data governance policies and procedures, ensuring they align with evolving business needs and industry standards. Implementing feedback loops, periodic audits, and staying attuned to technological advancements in data management contribute to the ongoing enhancement of data governance strategies.
This commitment to continuous improvement not only safeguards the integrity of customer master data but also enables the organization to respond effectively to changes in the data landscape, maintaining a robust and adaptive foundation for strategic decision-making.
Effective risk management within customer master data management involves implementing robust processes to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks associated with the handling of customer information. This includes ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and security of customer data to prevent errors, fraud, and unauthorized access.
A comprehensive risk management approach would also involve regular audits and monitoring to detect anomalies or irregularities in customer data, as well as establishing clear protocols for data governance and compliance with relevant regulations such as data protection laws.
By proactively addressing risks related to customer master data, organizations can enhance data quality, build trust with customers, and safeguard sensitive information, ultimately fostering a more resilient and secure customer data management environment.
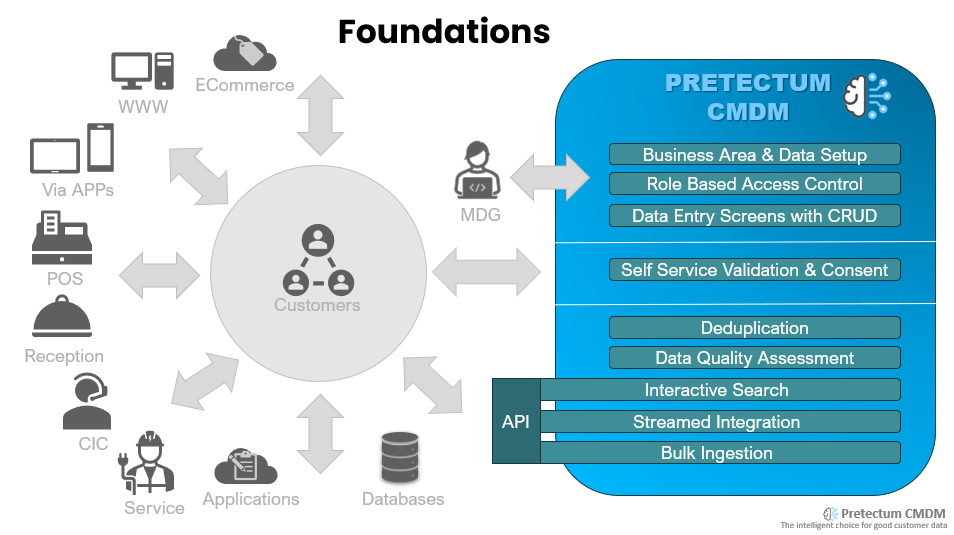
Evaluating a prospective source of truth
The criteria for selecting the right home for your CMDM initiative will revolve around the accuracy and integrity of data. Whatever you choose for CMDM it must incorporate robust validation mechanisms and quality checks to uphold the sanctity of customer data, preventing errors and discrepancies that might reverberate through the entire organizational structure.
Integration capabilities will likely play a crucial role in the CMDM selection process, whether it be in support of Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), or other systems. Such integration will ensure a unified and consistent view of the customer data, eliminating silos and fostering a panoramic perspective across the enterprise.
Scalability becomes the next checkpoint in the CMDM evaluation. Will your choice accommodate a likely ever-growing number of occupants? A CMDM solution must exhibit scalability to handle an expanding volume of customer data. If your business landscape is dynamic, then the chosen system should gracefully scale to meet the demands of your expanding enterprise without compromising performance.
Security measures are non-negotiable when dealing with customer data. The selected CMDM home should have robust security, actively defending against unauthorized access, monitoring for data breaches, and proactively looking out for cyber threats. For customer data, sanctity and confidentiality are paramount, you must make security a top priority for your CMDM abode.
Quite naturally, user-friendliness and the proverbial UXD (User Experience and Design) is often a pivotal criterion in any selection process. The experience should be intuitive and provide a user-friendly interface that supports employees’ easy navigation and interaction with the customer data. Such a system would foster user adoption through its design and navigational simplicity; enhance productivity and ensure that the benefits of CMDM permeate throughout the organizational structure.
Data governance should be centre stage. CMDM home must shelter and govern the data within its confines. A CMDM that comprehensively supports your data governance framework is imperative. You will want to be able to outline and enforce policies, standards, and processes for the entire lifecycle of customer data. This ensures internal consistency and compliance with external regulatory requirements, safeguarding the organization against legal ramifications.
Flexibility and customization emerge as key facets in this selection saga. Every organization has unique preferences and requirements. Your choice of CMDM solution should mirror this diversity, offering flexibility and customization options that align with specific business processes and evolving data management needs. The home for your customer data should not be an entirely rigid structure but rather an adaptable space that flexes with the unique rhythm of the organization it serves.
AI and Machine Learning Integration bring a futuristic dimension to the CMDM narrative. The idea of CMDM solutions leveraging AI and machine learning suggests opportunities to plumb the depths of the data with advanced data matching, deduplication, and predictive analytics. Such an infusion of intelligence would enhance the accuracy and utility of the customer master and provide insights that transcend traditional data management boundaries.
We believe that the Pretectum CMDM will address all of these expectations and provide you with some surprising additional ones. Contact us today to learn more.